How NB‑IoT and LTE‑M Fit into the IoT Ecosystem: The Future of Cellular IoT
August 31, 2018
 The Internet of Things
(IoT) will massively expand the use of cellular communications beyond
smartphones and tablets to an extraordinary range of applications and
connected devices — including many products that haven’t yet been
invented.
The Internet of Things
(IoT) will massively expand the use of cellular communications beyond
smartphones and tablets to an extraordinary range of applications and
connected devices — including many products that haven’t yet been
invented.
Although many IoT applications only need short-range wireless connectivity, a significant number will require longer-range connections. Examples include utility meters, sensors that monitor farm fields, or telematics modules tracking trucks on cross-country routes.
That’s where cellular IoT comes in, and specifically the two cellular IoT standards expected to dominate the market: NB‑IoT and LTE‑M. Let’s explore these two standards, their potential uses and some implementation options for device makers looking to add cellular connectivity.
Why we need NB‑IoT and LTE‑M
LTE‑M (Long Term Evolution for Machines) and NB‑IoT (narrowband Internet of Things) are standards created by 3GPP, the standards organization responsible for LTE and 5G. They let operators leverage existing cellular infrastructure to support very wide deployment of IoT devices. Because they operate in licensed spectrum, they’re secure, reliable and provide guaranteed quality of service.
Both LTE‑M and NB‑IoT fall under the category of machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, also known as machine-type communications (MTC). They help enable applications such as smart cities, environmental monitoring, asset tracking and more.
Of course, operators already use older 2G and 3G networks for some IoT applications, like fleet tracking. But LTE‑M and NB‑IoT are different because they’re specifically designed and optimized for IoT devices that communicate small amounts of data over long periods of time. So they’re simpler than other cellular standards, with much less overhead. This translates into:
- Very low power consumption, allowing device battery life of up to 10 years. That’s why these networks are also sometimes called low power wide area networks (LPWANs).
- Long range and very wide coverage — several times better than LTE.
- Low-cost hardware, due to the reduced complexity and economies of scale.
- Up to 100,000 or even more devices per base station, because each device has very low data-throughput requirements and because optimized software techniques let base stations communicate with very large numbers of IoT devices.
NB‑IoT and LTE‑M are the natural successors to older cellular standards for existing applications, and they’ll also drive development of completely new applications. Imagine if local governments could determine when waste bins need emptying, identify free parking spaces and automatically monitor environmental and road conditions.
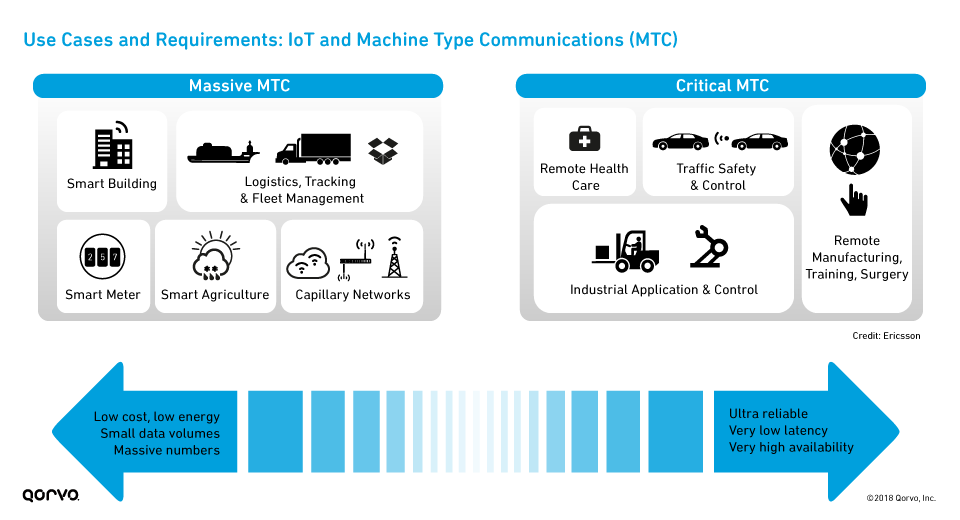
The following figure shows some of the IoT use cases enabled by massive MTC and critical MTC applications. Massive MTC relies on LPWAN technologies, including NB‑IoT and LTE‑M, while critical MTC will require real-time communications with very low latency and high reliability.
Differences between LTE‑M and NB‑IoT
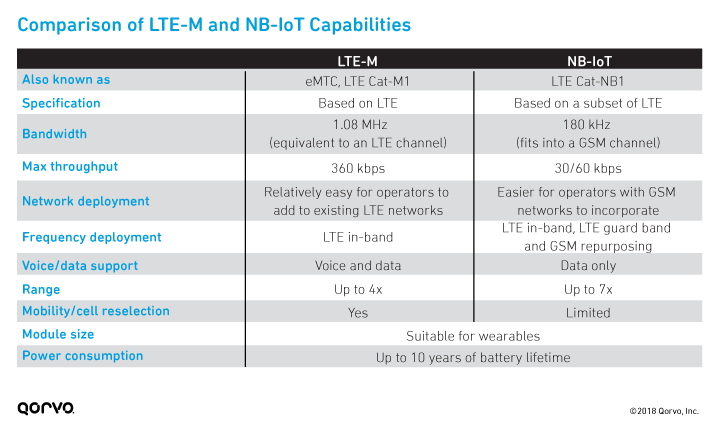
The following table compares the characteristics of LTE‑M and NB‑IoT. The biggest differences are bandwidth and voice support, but for practical purposes, the differences for IoT device developers are likely to be small. NB‑IoT may use slightly less power and the required hardware may be slightly less complex.
The momentum behind cellular IoT
Perhaps the biggest reason that NB‑IoT and LTE‑M are so important is their huge industry momentum. According to GSMA*, operators have launched 58 NB‑IoT and LTE‑M networks as of July 2018, establishing coverage in most major markets worldwide.
China has standardized on NB‑IoT, creating a potentially massive market that is likely to help drive development of IoT solutions. In the U.S., some operators (including Verizon and AT&T) launched LTE‑M networks first, but NB‑IoT networks are also planned.
In many cases, operators can implement cellular IoT networks simply through a software upgrade to their existing base stations. This means they can roll out broad coverage very quickly and at low cost.
Go in Depth
- Introduction to Narrowband Internet of Things (Rohde & Schwarz)
- T-Mobile Launches NB‑IoT Nationwide (FierceWireless)
- Verizon Taps Cat M1 Network for Smart Grid Utility Services (FierceWireless)
- Top 5 RF Technologies for 5G in the IoT (Microwaves & RF)
What matters to device makers?
Over the next few years, we’re likely to see thousands of companies design new products to take advantage of the opportunities opened up by cellular IoT. Here are some key considerations for device makers:
- It’s important to take into account the steps needed to gain the operator certifications required to connect to licensed networks. Leveraging the expertise of RF partners can help overcome this challenge.
- There will be a strong incentive to support both NB‑IoT and LTE‑M networks, to maximize potential sales. Fortunately, dual-mode chipsets are appearing that allow device manufacturers to build a single product for global deployment.
- Many IoT devices will be expected to work reliably in the field for up to 10 years without needing service. So cellular IoT components must be very reliable, and replacement parts must be available for a long time.
Qorvo’s portfolio of cellular IoT options for device makers
Qorvo applies its RF technologies and expertise to a broad range of cellular IoT solutions, including products for IoT connectivity in devices and base stations:
- Low-power RF front ends that enable devices to support LTE‑M and NB‑IoT.
- Dual-mode system-on-chip (SoC) for IoT devices. Qorvo has partnered with Nordic Semiconductor to develop a complete dual-mode NB‑IoT and LTE‑M solution designed to make it as simple as possible to build cellular connectivity into IoT devices.
- Base station products. Qorvo provides a portfolio of high-performance, off-the-shelf components, including amplifiers, switches and filters, to facilitate rapid deployment of IoT networks.
We’ve helped many companies achieve operator certification, and we supply industries such as automotive, aerospace and defense with very high requirements for product reliability and longevity.
Cellular IoT: Enabling billions of new connected devices
NB‑IoT and LTE‑M are just getting started. Over the next few years, these low-power cellular networks will open the door to a wealth of new applications, connecting billions of devices that need long-range connectivity combined with extended battery life. For makers of IoT devices, ensuring that products support both standards will maximize the opportunities.
For more information on Qorvo solutions for NB‑IoT and LTE‑M, check out our portfolio of IoT products.
*Note: Accessed as of 8/31/2018.
Have another topic that you would like Qorvo experts to cover? Email your suggestions to the Qorvo Blog team and it could be featured in an upcoming post. Please include your contact information in the body of the email.
